Maximum tree height in European Mountains decreases above a climate-related elevation threshold
Abstract
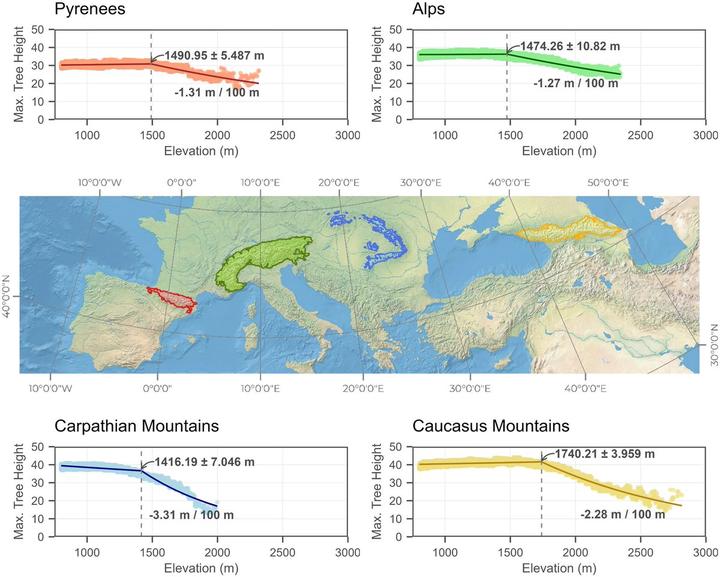
Mountain forests face important threats from global change and spatio-temporal variation in tree height can help to monitor these effects. In this study, we used the Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation space-borne laser sensor to examine the relationship between maximum tree height and elevation, and the role of climate, in the main European mountain ranges. We found a piecewise relationship between elevation and maximum tree height in all mountain ranges, supporting the existence of a common breakpoint that marks the beginning of tree development limitations. Temperature and precipitation were identified as the most important drivers of tree height variation. Additionally, we predicted significant upward displacement of the breakpoint for the period 2080-2100 under climate change scenarios, potentially increasing the area without growth limitations for trees. These findings contribute to understanding the impacts of global warming on mountain forest ecosystems and provide insights for their monitoring and management.